Navigating the complex world of information security requires a sound risk management strategy. Focusing on 8 key steps, this article explores how to establish an ISO 27001 risk assessment framework, create a comprehensive list of information assets, identify and analyse risks, and then develop a risk treatment plan.
By understanding these fundamental steps, organisations can strengthen their information security management systems, align with ISO 27001 standards and proactively protect their valuable assets.
Risk management is at the heart of implementing any information security procedure in your organisation. It is likely the most crucial yet challenging component in implementing the ISO 27001 Standard for information security. Risk management is composed of two elements: risk assessment and risk treatment.
An effective risk assessment identifies any risks your organisation may face, and risk treatment ensures your information security management system (ISMS) has the proper risk mitigation strategies and controls in place to handle them.
Without a clear understanding of risk management, organisations may find it challenging to implement the ISO 27001 standard and attain the certification. We’ve compiled a comprehensive guide to conducting successful risk assessments to help you.
Let’s briefly examine what risk management and assessments are before diving into the steps involved in conducting them.
What is information security management?
Information security risk management is the most critical component of the first stage of any information security project. Still, it can also be the most challenging aspect of your ISO 27001 implementation process. Simply put, risk management is your organisation's foundation for information security. Therefore,
- Define and document an appropriate method for identifying and assessing risks to the organisation.
- Define and document an appropriate and consistent process for treating identified risks.
- Assign responsibility and ownership to support effective risk management.
While removing all risks is impossible, you can reduce them to an acceptable risk threshold for your organisation through the assessment process.
Risk assessment or analysis and risk treatment are two fundamental elements of the risk management process. Let’s now see what risk assessments are.
What is information security risk management?
A security risk assessment provides a clear overview of the risks and vulnerabilities that may compromise the security of your information assets. It identifies and evaluates the application of essential security measures while preventing security flaws and vulnerabilities in them. Generally, risk assessments are conducted across the whole organisation.
The importance of information security risk management
An information security risk assessment provides your organisation with an understanding of the vulnerabilities and threats in your information security posture. This can aid your organisation in adopting a strategic approach to protecting your information assets. Risk assessments provide organisations with several benefits, including:
Define roles and responsibilities
The risk assessment can help organisations clarify the roles of staff involved with information security. Each person will know what is expected of them, and this can also help in managing access to sensitive information within the organisation.
Allocate resources strategically
Since the assessment can identify the vulnerabilities and existing controls in your information security management system (ISMS), you can allocate your resources more effectively, targeting specific risks rather than attempting to create a one-size-fits-all solution to the security flaws.
Respond effectively to security risks and breaches
Information security risk assessments can provide data that could help your organisation better protect itself against security breaches. This information may help you to deploy the most appropriate and effective measures against different threats to your information security.
The benefits of risk assessments are significant, so ISO 27001 considers them crucial in implementing the standard.
ISO 27001 and risks
With the ISO 27001 standard comes the need to regularly review, update and improve your ISMS. This means your organisation is acutely and consistently aware of the risks it faces regarding information security. It also ensures your ISMS constantly adapts to the evolving environment surrounding risks to information security assets.
Let’s take a deeper look into how the standard defines risks, treats risks, and helps with risk management.
How does ISO 27001 define risks?
ISO 27001 defines risk as the "impact of uncertainty on objectives." It is impossible to entirely control all the risks your organisation faces, but you can plan for this uncertainty through a Risk Treatment Plan (RTP).
How does ISO 27001 help with risk management?
The continuous assessment and management of your Information Security Management System (ISMS) and associated risks lies at the heart of ISO 27001. Clause 6.1.2 of ISO 27001 has five main criteria for the risk assessment process. You need to define:
- The identification of risks which could result in the loss of confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your information.
- The identification of risk owners.
- The criteria for the assessment of consequences and the likelihood of risk.
- The criteria for the calculation of risk.
- The criteria for the acceptance of risk
The standard specifies how to maintain best practices in your ISMS, which is geared towards managing risks to ensure your organisation’s information assets are protected.
Eight steps for an effective risk management
To meet the requirements specified by ISO 27001, your risk assessment process should consist of eight primary steps to be effective. Let's look at each step in detail to understand the best possible path to make your risk assessment a success.
1. Establish an ISO 27001 risk assessment framework
According to Clause 6.1.2 of ISO 27001, risk assessments should be “consistent, valid and comparable” every time they are carried out to be auditable, objective, and transparent. This is where a risk assessment framework comes into play. A framework provides a formal methodology for consistent results each time, even at the hands of different risk assessors.
The framework is a set of guidelines explaining how the risk assessment process is undertaken. It addresses four main concerns:
1. The most important security criteria for your organisation
Clauses 4.1 and 4.2 of ISO 27001 require your organisation to identify the business, regulatory and contractual obligations you have to meet about information security, known as the ‘baseline security criteria’. The review of the baseline security criteria is done using a risk assessment tool to ensure the necessary controls have been implemented to address them.
2. The scale of risk
In addition to the baseline security criteria, you should also establish the risk scale. A risk is defined by both the likelihood of it occurring and its impact on the organisation. The risk scale shows you how to analyse and respond to risks.
3. Risk acceptance criteria
Risk acceptance criteria refer to the levels of risk your business is willing to withstand. Companies must ensure they meet applicable statutory, regulatory, and contractual requirements when establishing risk acceptance criteria (also known as risk appetite).
4. Methodology (Risk assessment based on scenarios or assets)
Risk assessment is mostly done using two methods: scenario-based risk assessment or asset-based risk assessment. The methodology helps you outline your risk assessment framework and ensures a consistent approach throughout the organisation.
2. Create a list of your organisation’s information assets
Let’s take a detailed look at the most used methods of undertaking a risk assessment for your organisation:
1. Asset-based risk assessment.
An asset-based risk assessment focuses on the risk to an organisation's information assets. While it is a lengthy process, it provides a more comprehensive risk review.
Asset types to consider during an assessment include:
- Information and data
- Hardware and software
- Physical locations and storage
- Systems and services
- People and organisations
- Intangibles
An asset database can be a valuable tool in conducting the assessment. An asset database lets you easily classify and assign responsibility to each asset. Having an integrated and compatible asset database helps track asset-based risks over time.
2. Scenario-based risk assessment
A scenario-based risk assessment means your organisation concentrates on preparing for scenarios which could result in either a data breach or from preventing the organisation from being able to continue Business as Usual (BaU). While such a report will help you speed up the risk identification process, this method leads to users overlooking factors which could lead to risk.
The asset-based risk assessment provides a comprehensive overview of your organisation’s risk factors. After you list all your assets, the next step is to analyse the threats and vulnerabilities related to those assets.
3. Identify your risks
After consolidating your information assets, it’s time to identify the risks associated with them. Although it is a straightforward process, this step remains the most time-consuming. It is, however, vital in helping you prepare for risks.
To start identifying risks to your business, you need to understand your business processes and have oversight of your information security assets. Internal and external factors that could have an impact should also be considered. These areas will be assessed and documented earlier on in the project to act as a foundation for the ISMS, risk assessment and risk treatment.
The source of risks can be:
- An information asset
- An internal or external threat
- A vulnerability in the ISMS
You can identify risks by using:
- Expert knowledge within the organisation
- Previous security events, incidents and data breaches
- Results of internal and external audits
- Regulatory, legislative, or contractual requirements
The assessment is also the time to evaluate the effectiveness of your existing controls. Through this, you can avoid duplicating existing measures and implementing redundant controls.
It is essential also to determine the timeframe of risk assessment and the internal parties to be involved. This is because risks need to be allocated to owners. These owners should be included in the risk assessment process as they will have the necessary knowledge to provide the required information to support it.
Establishing the timeframes for risk assessment can ensure timely action. More comprehensive risk assessments should also be held regularly to identify and capture new risks in the risk matrix.
4. Analyse your risks
After the risks associated with each asset are identified, the next step is risk analysis. Assets may have several threats which can be exploited via multiple vulnerabilities in your system. It is important to assess the likelihood of each combination of threat and vulnerability and their impact during the risk assessment.
After analysing how threats may exploit the individual vulnerability, you can assign a score to each event to quantify your assessment. The outcomes of the analysis should also be reflected in the Risk Assessment and Treatment Table.
5. Evaluate risk impact
After analysing the risks, it is essential to understand which risks could do the most damage. Ranking risks based on their impact and their likelihood would help your organisation deploy its resources effectively and reduce redundancy. Through this, you can determine which hazards must be prioritised and controlled immediately to prevent a possible security breach.
Overall Risk = Likelihood x Impact
The likelihood of risks affecting your business can be determined as follows:
| Level | Label | Description |
| 1 | Insignificant | The probability of the risk occurring is insignificant, but there is a chance it could happen. |
| 2 | Low | The probability of the risk occurring is low, but there is a chance it could happen. |
| 3 | Medium | The probability of the risk occurring is moderate, indicating a reasonably likely chance. |
| 4 | High | The probability of the risk occurring is high, meaning there is a significant likelihood. |
| 5 | Catastrophic | The probability of the risk occurring is extremely high and should be considered an expected occurrence. |
The impact those risks might have on your business can be ranked as follows:
| Level | Label | Description |
| 1 | Insignificant | The probability of the risk occurring is insignificant, but there is a chance it could happen. |
| 2 | Low | The consequences of the risk are relatively minor, resulting in a slight impact. |
| 3 | Medium | The consequences of the risk are moderate and could cause notable disruptions. |
| 4 | High | The consequences of the risk are significant, leading to substantial disruptions or losses. |
| 5 | Catastrophic | The consequences of the risk are severe and could result in complete system failure, impacting organisational operations. |
A tool which can help with risk evaluation is a risk matrix. A risk matrix will have two axes, one which shows the likelihood of a risk occurring while the other axis represents the consequences.
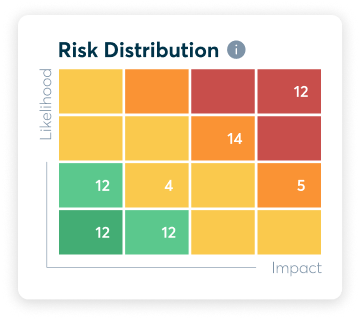
The results of the risk matrix can help determine which risks you will prioritise addressing. In addition, it can assist in determining your organisation’s risk acceptance criteria. By determining your risk acceptance criteria, you can decide on the risk treatment plan for each risk.
However, before moving onto the risk treatment stage, you will need to create a Statement of Applicability to provide the certification body with a clear understanding of your organisation’s security profile.
6. Create a statement of applicability (SoA)
The Statement of Applicability (SoA) depicts your organisation’s security profile.
It shows:
- The controls you have chosen to address your identified risks
- Your reasons for the controls you have selected
- The controls you have implemented
- How you have implemented the said controls
- Your reasons for omitting any of the ISO 27001 Annex A controls
The certification body uses the SoA as the primary guideline for the audit. It is fundamental for the ISO 27001 certification and is one of the first things an auditor uses when assessing your organisation. It is also extremely useful for everyday operational use, providing your organisation with several benefits.
An SoA:
- It gives a broad perspective into the organisation’s actions to protect its information. This helps identify, organise, and document your security measures and traces the controls of the standard in relation to what is done in the organisation.
- It provides a rationale for the inclusion or exclusion of each control.
- It shows your defences from an ISO 27001-compliant risk assessment in the event of an investigation into a data breach.
- It helps your organisation prioritise expenses.
- It reduces the need for certain other documents.
After creating the SoA, it’s time to assemble a Risk Treatment Plan (RTP).
7. Create a risk treatment plan
After identifying and ranking the risks, the next step is creating a Risk Treatment Plan (RTP) to manage them. The RTP is an action plan detailing how your organisation will implement controls to handle the risks. It specifies the controls to be implemented and the responsible parties, the planned deadlines and the required resources.
Risk is usually treated in the following four ways and is known as the TARA (Transference, Avoidance, Reduction or Acceptance) Framework.
Transference
Taking steps to transfer risks to a third party is a popular strategy for mitigating risks which would have a high impact on the organisation but a low likelihood of occurrence. By sharing the risks, most or all the damages would be borne by the third party in the event of its occurrence. A cyber insurance policy is a common way to transfer information security risks.
Avoidance
Completely avoiding risks is a strategy employed when the impact and likelihood of occurrence are high. Often, this means the organisation would completely divest from the activity since certain risks are unavoidable in business.
Reduction/Mitigation
Risk reduction helps you mitigate the adverse impact in case of occurrence or reduce the likelihood of its occurrence. Here’s where implementing controls, strengthening your information security posture and continuously improving your ISMS come in.
Acceptance
In the case of risk acceptance, you consciously acknowledge and tolerate certain identified risks without implementing specific risk treatment measures. Here, you recognise that some risks may persist after existing controls but are within acceptable limits.
Risk acceptance is when a company states, "We know these risks are there, but we accept them. We won't spend extra time or money to fix them right now." The decision is made after looking at how likely and impactful each risk is. The choice must be thought out and match the company's goals and resources.
In contrast, risk avoidance is when a company says, "We're steering clear of anything that seems risky." So, risk acceptance is being aware of risks and deciding to live with them, while risk avoidance is actively avoiding situations that could be risky altogether.
Risk treatment plan key takeaways
The Risk Treatment Plan is the output of the risk assessment process and is typically written after the Statement of Applicability. The plan may include other details such as timelines for each stage, the resources available, and management approval. The plan should also note the residual risk levels to be accepted after completion.
Risk management shifts from a theoretical concept to a practical plan in the RTP.
Documenting and completing these plans will provide evidence effort is being made to achieve your ISMS objectives (a requirement of the ISO 27001 Standard). Documenting risks will also support the monitoring and measurement of business performance.
8. Review, monitor and audit internally
With information security threats and your organisational functions evolving constantly, risk assessments should be repeated annually. This can help you stay on top of any new vulnerabilities and threats and account for them. Continuous improvement is at the core of ISO 27001, and risk assessment can improve your ISMS.
The review process can be broken down as follows.
Employee accountability and awareness
ISO 27001 states it is essential to identify the risk owners for each risk. They are responsible for approving any mitigation strategies and accepting the residual risk level. Getting your employees involved in the risk management process and understanding their feedback could help you identify vulnerabilities and refine your process.
Management reviews
Regularly reviewing risks is essential to a good risk management process, and reviews are recommended to be annual at the very least. The ISO 27001 Standard requires regular management reviews to take place. Since each risk is different, we recommend you review risks based on priority. For example, critical risks could be reviewed monthly, while low likelihood and impact risks can be covered in the annual reviews.
Internal audits
Regular internal audits are another requirement of the Standard and help you ensure that your ISMS is working effectively. The Risk Management process will be reviewed as part of this to ensure ongoing compliance.
Expert support
The risk management process is a continuous one and may seem daunting at first glance, especially if you are not familiar with it. Expert support can streamline the process for you and your organisation.
The advantage: external services can be purchased quickly and do not require a long onboarding process thanks to the service provider's wealth of experience. A good provider assigns its customers a personal contact who is familiar with the customer's current challenges and has already mastered them elsewhere.
If you feel overwhelmed by the complexity of implementing effective risk management, talk to one of our experts. We speak your language and can help you with every step to make your risk assessment a success.









